Ever placed an order for something online, only to find the price has jumped up by a few cents by the time you get to the checkout? That’s slippage in a nutshell.
In the fast-moving world of trading, slippage is simply the difference between the price you think you’re getting and the price you actually get when your trade goes through.
What Is Slippage, Really?

At its heart, slippage happens because the price you click isn't always the price you get. There's a tiny, almost instantaneous delay between when you hit "buy" or "sell" and when the exchange actually fills your order. In that fraction of a second, the market can move.
Now, slippage isn't always a bad thing. It can be negative (costing you money), positive (saving you money), or even zero. It’s most common in highly volatile markets like crypto, or when there isn’t enough trading volume (low liquidity). This is why you'll often see it discussed in contexts like spread betting, where market conditions are key.
To become a savvy trader, you have to nail these foundational concepts. For more deep dives like this, the VTrader Academy is packed with resources to get you up to speed.
Slippage at a Glance
To make it even clearer, let's break down how a simple trade can be affected by slippage. This table shows the moving parts of a single transaction.
| Concept | Simple Explanation | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Expected Price | The price you see when you decide to place your trade. | You want to buy Bitcoin at $60,000. |
| Executed Price | The actual price your trade is completed at. | Your order is filled at $60,025. |
| Negative Slippage | You get a worse price than you expected. | You paid $25 more per Bitcoin than planned. |
| Positive Slippage | You get a better price than you expected. | Your order is filled at $59,975. |
As you can see, the same trade could result in you paying more, less, or exactly what you expected, all thanks to those tiny price shifts that happen in the blink of an eye.
The Market Forces That Cause Slippage
Slippage isn't some random glitch; it's a direct consequence of the market's inner workings. To really get a handle on what slippage is, you first have to understand the two main culprits behind it: high volatility and low liquidity. These two forces often team up to create that frustrating gap between the price you click and the price you actually get.
Think of volatility as how fast prices are bouncing around. In a highly volatile market, prices can swing wildly in just a few seconds. It’s like trying to hit a fast-moving target—by the time your order makes its way to the exchange, the price may have already darted up or down, forcing your trade to execute at a different level.
The Role of Market Liquidity
Liquidity, on the other hand, is all about how many buyers and sellers are in the market at any given moment. A market with high liquidity is like a massive, bustling supermarket. There are plenty of products (assets) on the shelves and shoppers (traders) ready to buy and sell. Orders get filled almost instantly because there's always someone on the other side of the trade.
Now, imagine a small town shop with just a few items and even fewer customers. That's a low-liquidity market. If you try to place a large order, you might find yourself buying from multiple sellers at increasingly higher prices just to get your full order filled. In this small pond, your big order makes waves, pushing the price against you and creating slippage.
The relationship here is crystal clear: Illiquid markets with low trading volume or shallow order books almost always have wider bid-ask spreads. This makes them far more prone to significant slippage. Throw in high volatility, especially during major news events, and you have a perfect storm.
This infographic really breaks down how these factors play off each other to cause slippage.
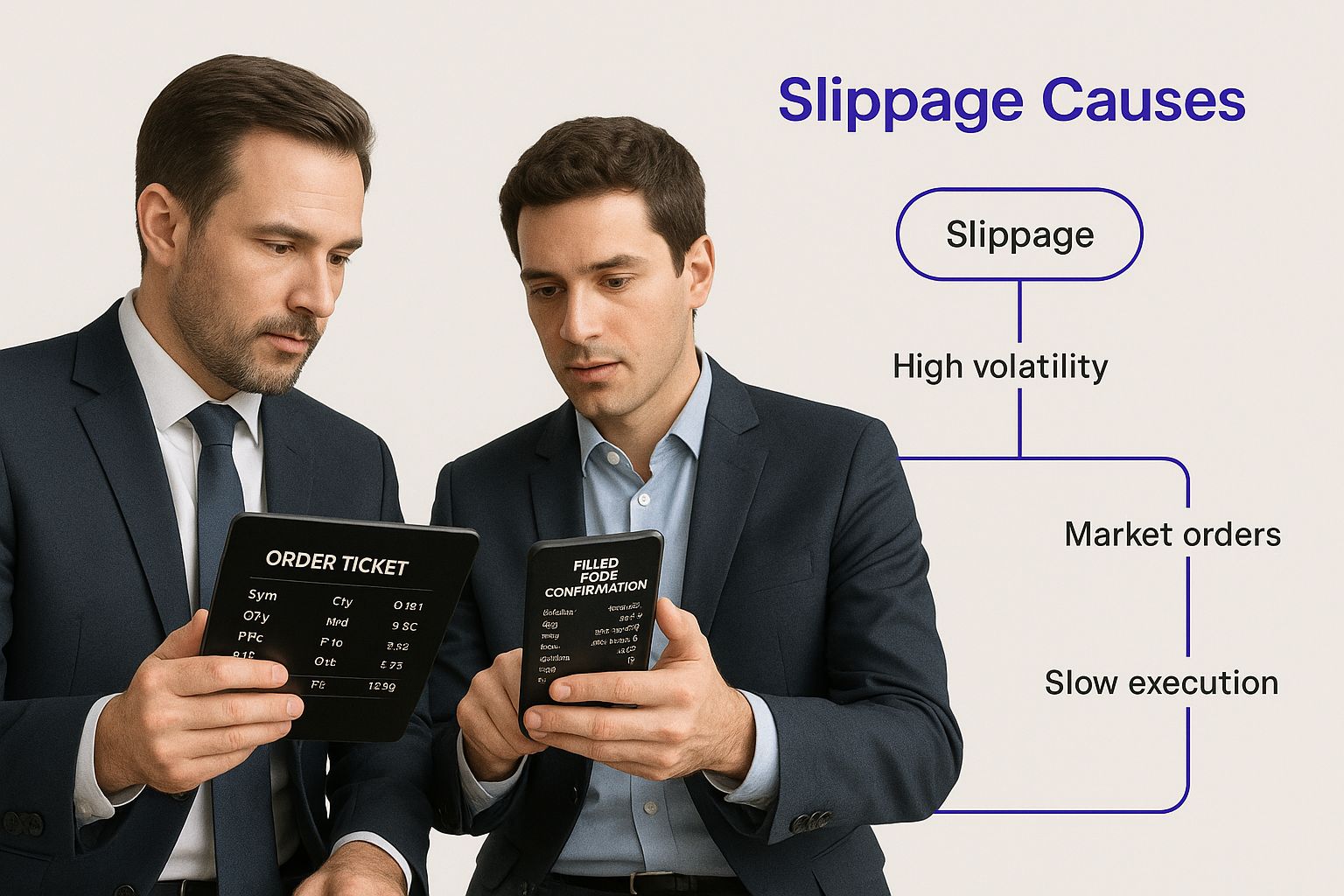
As you can see, slippage isn't a single problem but a result of the dance between market speed and the depth of available orders. When volatility is high and liquidity is low, your risk of slippage is at its absolute peak. This is especially true during major economic announcements or geopolitical events, which can turn market conditions on their head in an instant. You can keep up with how market events are influencing trading on our vTrader news page.
Getting a grip on these forces is the first step toward managing them. Once you know what you’re up against, you can start building a strategy to protect your trades.
Seeing Slippage in Real-World Trades
Theory is one thing, but seeing how slippage plays out with real money is what makes the concept click. Let’s walk through a few scenarios that show how this "price drift" can affect your trades, sometimes for the better, but often for the worse.
Example 1: Negative Slippage on a Buy Order
Picture this: You’re watching Ethereum (ETH), and the price hits a perfect $3,000. You jump on it, placing a market order to buy 10 ETH. In your head, the math is simple: $30,000.
But the market is on fire. In that blink-of-an-eye moment between your click and the trade’s execution, a flood of buy orders hits the market. Your order gets filled, but at an average price of $3,003 per ETH.
- Expected Cost: 10 ETH x $3,000 = $30,000
- Actual Cost: 10 ETH x $3,003 = $30,030
- Negative Slippage: $30
That tiny $3 price difference per coin just cost you an extra $30. It might not seem like much here, but imagine that on a larger scale or during even more intense volatility. It adds up fast.
Example 2: Positive Slippage on a Sell Order
Now, let's flip the script. You’re ready to take profits on 20 Solana (SOL) tokens. The market price is sitting at $150, so you place a sell order, expecting to bank $3,000.
Right as you hit sell, a whale-sized buy order sweeps through, nudging the price up just for a second. Your order fills at an average price of $150.10.
- Expected Proceeds: 20 SOL x $150 = $3,000
- Actual Proceeds: 20 SOL x $150.10 = $3,002
- Positive Slippage: $2
In this case, slippage actually worked in your favor, dropping an extra $2 into your pocket. It’s a pleasant surprise when it happens, but it's definitely less common than its negative counterpart.
Example 3: High Slippage with a Low-Liquidity Altcoin
Finally, let’s look at where things can get really messy. A brand new altcoin, let's call it "NewCoin," is trading at $0.10. You decide to go in big with a $5,000 buy, which should land you 50,000 tokens.
But this coin is new and has very low liquidity—there just aren't many people selling. Your huge buy order chews through all the available sell orders, pushing the price higher with every token it buys. Your average price skyrockets to $0.12.
- Expected Tokens: $5,000 / $0.10 = 50,000 NewCoin
- Actual Tokens: $5,000 / $0.12 = 41,667 NewCoin
- Slippage Cost: 8,333 fewer tokens
This is the classic low-liquidity trap. Your own trade was so large relative to the market that you moved the price against yourself, leading to a staggering 16.7% loss in expected assets before you even held the coins. This is exactly why understanding a market's depth is non-negotiable.
How Slippage Quietly Drains Your Profits
It’s one thing to know the definition of slippage, but truly understanding it is about protecting your capital from what is essentially a hidden tax on every trade you make. A single instance of negative slippage might feel like nothing—just a few cents. But its real danger is how it adds up.
Think of it like a tiny, slow leak in a boat. One drop is meaningless, but over time, hundreds of those drops will leave you sinking. That’s exactly how slippage chips away at your portfolio. A small loss here and another there can quickly compound, turning what should have been a profitable strategy into a break-even—or even losing—endeavor.
How Volatility Pours Fuel on the Fire
This problem gets exponentially worse when the market is under stress. A painful, real-world example of this unfolded during the market chaos of March 2020. As panic over the COVID-19 pandemic sent shockwaves through the financial world, volatility shot through the roof while liquidity all but dried up.
In that period, many systematic trading strategies saw their slippage rates jump to two or three times what they normally were. You can get a better sense of how these conditions impact trades from this in-depth analysis on managing slippage. For many traders, that spike was enough to completely wreck their otherwise sound models.
This teaches a crucial lesson: slippage isn't just another trading fee. It's a variable cost that can spiral out of control when you least expect it. Ignoring it is like trying to trade with a blindfold on, completely unaware of the small losses that are steadily eating away at your bottom line.
The biggest threat from slippage isn't one huge, catastrophic loss. It's the silent, consistent drain on your profits from dozens of seemingly minor mispricings that can crush your capital in the long run.
For any serious trader, actively managing this "cost" isn't just a good idea—it's a fundamental part of risk management and survival in the markets.
Actionable Strategies to Minimize Slippage
You can't ever get rid of slippage completely—that's just the nature of the beast. But you can absolutely take the reins and minimize how much it chips away at your portfolio. Knowing what is slippage in trading is only the first step; the real game is using smart tactics to keep your capital safe.
Your single most powerful weapon against slippage is the limit order. A standard market order is like shouting "buy at any price!" into the void. A limit order, on the other hand, lets you draw a line in the sand. If you want to buy Bitcoin at $60,000, a limit order makes sure you won't pay a single cent more.
Adjust Your Trading Habits
Beyond the type of order you place, your timing and trade size are huge factors. Volatility is a breeding ground for slippage, so one of the simplest—yet most effective—strategies is to just sit on your hands when the market gets chaotic.
- Avoid Major News Events: Trying to trade moments before or after a big announcement, like an interest rate decision or a major project launch, is asking for trouble. Liquidity often vanishes, creating the perfect storm for slippage.
- Break Up Large Orders: If you're looking to move a large amount of crypto, especially on a less liquid pair, don’t drop it all at once. Splitting a big trade into several smaller chunks can stop your own order from pushing the price against you.
A limit order gives you price certainty, but it doesn't guarantee your order will actually get filled. If the market zips right past your price, you might be left on the sidelines. It's the classic trade-off: guaranteed price versus guaranteed execution.
Fine-Tune Your Slippage Tolerance
Many platforms, especially decentralized exchanges (DEXs), give you direct control over your slippage tolerance. This setting lets you tell the platform the maximum price change you're willing to swallow. Setting it to 1%, for example, means your trade will only go through if the final price is within 1% of what you expected.
Choosing a platform with a transparent fee schedule also helps you see the full picture of your trading costs. When you understand every potential charge, you can better anticipate how they'll interact with slippage. You can check out a clear example of this in vTrader’s fee policy. By combining these strategies, you'll go from being a victim of slippage to a trader who actively manages and controls it.
How vTrader Helps You Control Slippage

While the strategies we’ve covered are crucial, your greatest ally in the fight against slippage is often the trading platform you use. Proactive traders need tools built to tackle these challenges head-on. This is where vTrader’s architecture gives you a real edge, moving beyond basic order types to offer built-in protection against those hidden costs.
Instead of just reacting to slippage after the fact, our platform gives you the intelligent features needed to manage it before it ever eats into your returns.
Smart Tools for Smarter Trading
We’ve integrated several key technologies directly into vTrader to minimize price discrepancies and protect your capital. Think of them as your personal trading assistants.
-
Advanced Slippage Calculator: Before you even hit “buy,” this tool gets to work. It analyzes current market volatility and liquidity to estimate your potential slippage costs, giving you a crystal-clear picture of your total execution cost upfront. No more guessing games.
-
Smart Order Routing: You don’t have to hunt for the best liquidity. Our system automatically scans multiple liquidity pools to find the deepest and most stable source for your specific trade. This massively reduces the risk of price impact by executing your order where it’s least likely to make waves.
-
Automated Order Splitting: Placing a large order? vTrader can automatically break it into smaller, optimized chunks. This is how you fly under the radar in thin markets, preventing your own trade from creating the very slippage you’re trying to avoid.
These aren't just fancy add-ons; they are core components designed to give you direct control over your trade execution. They all work together to safeguard your profits from the silent erosion of slippage.
The team behind these features is completely dedicated to building a fair and transparent trading environment. You can get a better sense of what drives these innovations by reading about the philosophy behind vTrader.
At the end of the day, the right platform doesn’t just execute your trades—it protects them.
Answering Your Questions About Slippage
Now that we've broken down what slippage is and how to handle it, let's tackle a few common questions that pop up all the time. Think of this as your go-to cheat sheet for anything slippage-related.
Your Slippage Questions Answered
Here are some of the most frequent questions traders have, with clear, straightforward answers.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can You Completely Avoid Slippage? | In short, no. It's an inherent part of any live market with moving prices. But you can absolutely manage it. Using limit orders, avoiding trades during chaotic market news, and picking a platform with solid execution tools are your best defenses. The goal is to minimize its impact, not to chase the impossible dream of eliminating it entirely. |
| Is Slippage Always a Bad Thing? | Surprisingly, no. While we usually focus on negative slippage (where you get a worse price), you can also get lucky with positive slippage. This is when your order fills at an even better price than you clicked for, handing you a small, unexpected profit. It’s a welcome surprise when it happens. |
| What Is Slippage Tolerance? | This is a feature, especially on DEXs, that acts as your personal safety net. You set a maximum percentage of price change you're willing to accept. If the market moves against you beyond that threshold before your order can fill, the trade is automatically canceled. It puts you in control of how much risk you're willing to take. |
The key takeaway is that slippage is simply the difference between the expected and executed price—it can be negative, positive, or zero.
These are just a few of the basics. For a deeper dive into more specific questions, feel free to check out the official vTrader FAQ page.
Ready to trade smarter, not harder? With vTrader, you get access to advanced tools designed to minimize slippage and protect your capital, all with zero commission fees. Start trading with vTrader today!

Steve Gregory is a lawyer in the United States who specializes in licensing for cryptocurrency companies and products. Steve began his career as an attorney in 2015 but made the switch to working in cryptocurrency full time shortly after joining the original team at Gemini Trust Company, an early cryptocurrency exchange based in New York City. Steve then joined CEX.io and was able to launch their regulated US-based cryptocurrency. Steve then went on to become the CEO at currency.com when he ran for four years and was able to lead currency.com to being fully acquired in 2025.


