Stripped down to its core, hash rate is the total combined computational power being used to mine and process transactions on a Proof-of-Work blockchain like Bitcoin. Just think of it as the network's engine—a measure of how many guesses it can make per second to solve a complex puzzle.
The Engine Powering the Blockchain

Picture millions of specialized computers across the globe, all firing away in a relentless race. They’re all trying to be the first to solve a ridiculously complex mathematical puzzle.
The winner gets the right to add the next "block" of transactions to the blockchain and, more importantly, gets rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency for their effort. The hash rate is simply the metric we use to measure the raw speed of this worldwide competition.
A higher hash rate is a sign of a healthy, secure network. It means more miners are participating, which makes it incredibly expensive and difficult for any single person or group to mess with the blockchain. This collective muscle is really what underpins the network's integrity.
Measuring Digital Horsepower
To really get a feel for hash rate, you have to understand the sheer scale we're talking about. The numbers are mind-boggling, so we use special units to keep them from looking like a phone number. What started with a few thousand hashes per second in Bitcoin's early days has exploded into figures that are almost hard to imagine today.
A higher network hash rate directly translates to greater security. It raises the cost and difficulty for a malicious actor to launch an attack, effectively creating a powerful economic deterrent that protects the entire ecosystem.
To put this immense power into perspective, let's break down the units used to measure it.
Understanding Hash Rate Units at a Glance
This table gives you a quick reference for the different units of hash rate, from the smallest to the absolutely massive. You'll see these abbreviations pop up all the time when discussing mining.
| Unit | Abbreviation | Hashes per Second |
|---|---|---|
| Kilohash | KH/s | 1,000 |
| Megahash | MH/s | 1,000,000 |
| Gigahash | GH/s | 1,000,000,000 |
| Terahash | TH/s | 1,000,000,000,000 |
| Petahash | PH/s | 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| Exahash | EH/s | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
As you can see, the jump from kilohashes to exahashes is huge, and it perfectly illustrates the incredible growth and fierce competition within the mining world.
This computational race is the foundation of how these networks agree on what's true. To go deeper, you can dive into the intricacies of blockchain consensus mechanisms. And if you're looking to build up your knowledge on other core crypto concepts, our VTrader Academy is packed with resources. Continue your learning journey here: https://www.vtrader.io/en-us/academy.
How Mining Translates Hashes into Blocks

Alright, let's pull back the curtain on how mining actually works. Forget the puzzle analogy for a second and get into the real mechanics. Miners are running powerful, purpose-built computers—you’ll hear them called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits)—that do one thing really, really well: perform a hashing function.
This function grabs a batch of transaction data from the network and essentially scrambles it into a unique, fixed-length code. This code is the hash.
Think of it like a digital fingerprint for that specific block of data. If you change even a single comma in the original data, the resulting hash, or "fingerprint," becomes completely unrecognizable. It’s a whole new code.
But miners aren't just creating any old hash. They’re on a mission to find one that meets a very specific condition set by the network—usually, it has to start with a certain number of zeros. This is where the brute-force guessing game begins. Miners toss in a random piece of data (called a nonce) and hash the block over and over again, trillions of times, until they land on that lucky, valid result.
Individual Power vs Network Strength
This frantic search for the right hash is exactly why the hash rate is the single most important metric in the game. An individual miner’s hash rate tells you how fast their machine can guess—how many hashes it can generate every second.
To put that into perspective, a top-tier machine like the Bitmain Antminer S21 Pro can pump out an astonishing 234 trillion hashes per second (234 TH/s).
That incredible speed is what makes a miner profitable, but it’s only half the story.
The total network hash rate is the combined firepower of every single miner on the blockchain. It’s a measure of the collective effort being thrown at finding the next block. A single miner's chance of solving the puzzle is simply their personal hash rate measured against the total network hash rate.
While a single miner's powerful hardware increases their chances of winning the block reward, it's the massive combined hash rate of the entire network that creates the security and stability everyone relies on.
Here’s a simple way to think about it:
- Individual Hash Rate: This is how many lottery tickets a single miner buys for each new block's raffle.
- Network Hash Rate: This represents the total number of tickets sold for that same raffle.
The more "tickets" you buy (a higher hash rate), the better your odds of winning the prize—newly created coins and transaction fees. This reward is the core incentive that keeps miners contributing their computing power, and in doing so, they secure the entire network for everyone.
If you’re curious about the value of those rewards, you can track the real-time prices of major coins. Learn more about the price of BTC and its market movements on our platform. At the end of the day, a miner's hash rate is what defines their shot at success.
Why a High Hash Rate Is the Ultimate Shield
Hash rate isn't just another performance metric; it's the very backbone of a blockchain's security. A powerful network hash rate acts like a digital fortress, making it absurdly expensive and difficult for anyone to mess with the network's integrity. The higher the hash rate, the thicker the walls.
This all comes down to thwarting something called a 51% attack. To successfully rewrite the blockchain's history—say, to reverse a transaction and double-spend coins—an attacker needs to control more than half of the entire network's computing power.
It’s like trying to win a global election single-handedly. You wouldn't just need a lot of votes; you'd need to cast more votes than every other voter on the planet combined. For a massive network like Bitcoin, pulling this off is practically science fiction.
The Economics of an Attack
Getting that much hashing power isn't just a technical problem—it's an economic impossibility for any sane attacker. The costs are absolutely staggering and serve as the best deterrent.
A would-be attacker would have to:
- Buy the Gear: Get their hands on hundreds of thousands of the most powerful mining rigs on the market, a logistical and financial nightmare.
- Pay the Power Bill: Find and pay for enough electricity to run this colossal mining farm, which would slurp down more energy than a small country.
- Beat the Network: Continuously out-compute the honest majority of miners, a group that's always growing and getting stronger.
This infographic breaks down how a high hash rate directly translates into rock-solid network security.
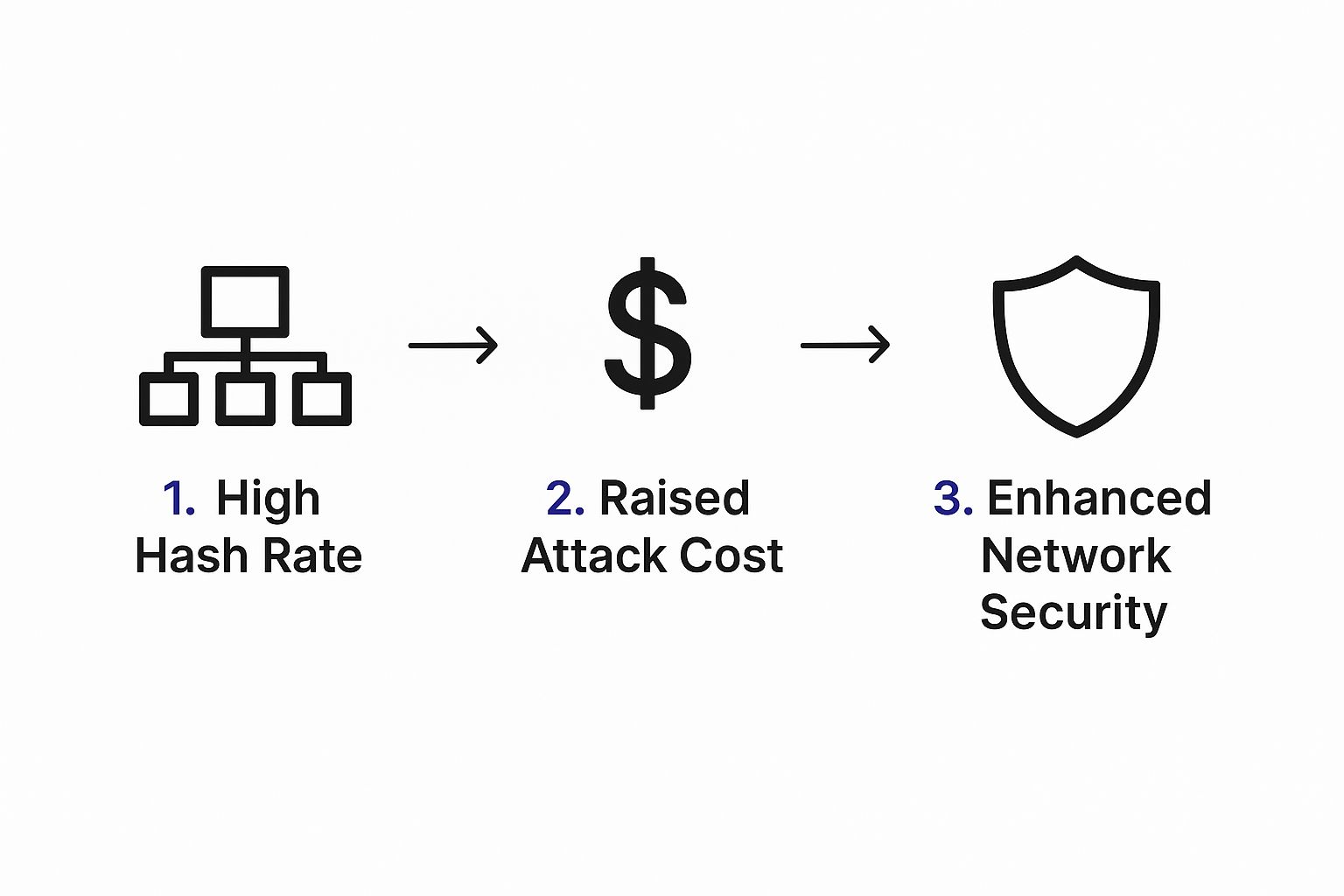
As you can see, the sheer cost to launch an attack on a network with a high hash rate makes it an economically irrational move.
Even if someone could jump through all those hoops, the second the attack went public, the price of the crypto they were trying to steal would almost certainly crash. This kills the very financial incentive that would drive such an attack in the first place.
A high hash rate makes cheating prohibitively expensive. This simple fact ensures it's always more profitable for miners to play by the rules and support the network than to try and tear it down. It creates a powerful, self-policing system built on economic incentives.
This brilliant defense mechanism is what makes Proof-of-Work blockchains so tough. Every miner contributing their hash power isn't just hunting for a reward; they're actively casting a vote for the network's security, making the digital fortress stronger with every single hash they compute.
Balancing Hash Rate, Difficulty, and Profit
A miner's hash rate doesn't operate in a bubble. It’s a key piece in a brilliant, self-regulating system that keeps the blockchain ticking along with predictable precision. The whole thing hinges on a concept called mining difficulty, which constantly adjusts based on the network's total hash rate. The goal? To keep the time it takes to find a new block steady—for Bitcoin, that’s about every 10 minutes.
Think of the mining puzzle like a massive digital combination lock. When not many miners are online and the network's hash rate is low, the lock might only have a few dials, making it relatively easy to crack. But as thousands of new, powerful miners jump in and the total hash rate skyrockets, the network adds more dials. The combination suddenly becomes exponentially harder to guess.
This difficulty adjustment is the blockchain's built-in cruise control. If a bunch of miners suddenly log off and the hash rate drops, the difficulty automatically lowers to make sure blocks don't take forever to find. If miners flood the network, it cranks up the difficulty to prevent blocks from being discovered too quickly.
The Constant Dance of Profitability
This elegant system creates a constant dance between a miner's personal hash rate, the overall network difficulty, and their bottom line. Even if you have the fastest hardware on the market, your earnings get squeezed when network difficulty rises because your slice of the total hashing power gets smaller.
This forces miners into a relentless chase for efficiency, where every single watt of electricity is scrutinized. The explosive growth of Bitcoin’s hashrate is directly linked to its massive energy consumption. To put it in perspective, a large public mining operation spent around $35,508 in power costs just to mine a single Bitcoin in early 2025. This cutthroat competition means mining difficulty just keeps climbing, with values soaring past 146 trillion by October 2025. You can find more insights on Bitcoin's energy use and its environmental impact on Statista.com.
A miner's success is a moving target. It’s not just about having a high hash rate, but maintaining a profitable balance between hardware efficiency, rising network difficulty, and volatile energy costs.
To stay in the green, a miner has to constantly juggle these key factors:
- Hardware Efficiency: This is measured in joules per terahash (J/TH) and tells you how much power a machine eats up to produce a certain hash rate. The lower, the better.
- Energy Costs: The price you pay for electricity is almost always the biggest operational expense. It can single-handedly make or break a mining operation.
- Cryptocurrency Price: At the end of the day, the market value of the coin you're mining dictates the real-world value of your block rewards.
This intricate balance is also why transaction fees—the other part of a miner's reward—are so important. Getting a handle on these costs, like we explain in our guide on the Ethereum gas tracker, helps you see the full economic picture that drives miners to participate in the network.
The Global Shift in Mining Power
The story of the global hash rate is one of explosive growth. It’s hard to believe it started with just a few crypto enthusiasts running software on their laptops. Today, it’s a multi-billion dollar industry with massive, specialized data centers humming away across the globe.
This journey saw the network’s computing power skyrocket from a few thousand hashes per second to numbers so large they're almost incomprehensible—we're talking quintillions.
But this growth isn't just about better tech. The map of where all this mining power is located has always been in flux, shifting in response to things like energy prices, government regulations, and political stability. Following the hash rate is like following the money and the power in the crypto world.
For a long time, China was the undisputed king of Bitcoin mining. Thanks to ridiculously cheap electricity and being the world's hardware factory, it controlled the lion's share of the global hash rate. This dominance, however, made a lot of people nervous about centralization and the risk of government interference.
The Great Mining Migration
Those fears became reality in 2021. The Chinese government launched a massive crackdown, effectively banning cryptocurrency mining overnight. What followed was a historic event dubbed the "great mining migration." Miners literally packed up their machines and fled, desperately searching for new, crypto-friendly homes.
This was a seismic event that completely redrew the world's mining map. Suddenly, North America—and the United States in particular—became the new hot spot. With a stable political climate and the infrastructure to handle huge energy demands, it was the perfect landing spot for the displaced mining industry.
Hash rate is more than just a technical metric; it's a powerful indicator of capital flows, regulatory sentiment, and the global competition for digital asset supremacy.
The dust has settled, but the map is still changing. The biggest takeaway? The network is far more decentralized now than it ever was during China's reign. It’s a testament to how quickly this industry can pivot and adapt.
A New World Order for Hash Rate
The aftermath of the migration solidified North America's role as the new leader. By 2025, U.S.-listed mining companies alone were estimated to control a whopping 38% of the global Bitcoin hash rate. The financial markets noticed, too. The combined market cap of these public mining firms hit a record $79 billion in October 2025. You can get the full story on this dramatic market shift on Coindesk.com.
This new landscape proves a simple truth: hash rate follows friendly laws and cheap power. Besides the U.S., a few other regions have also cashed in on the migration:
- Kazakhstan: Its proximity to China and low energy costs made it an obvious first stop for many miners.
- Canada: A cool climate and tons of clean hydroelectric power make it a miner's dream.
- Russia: Another country with cold weather and surplus energy that attracted significant mining operations.
This global shuffle is far from over, and it’s a fascinating trend to watch. To keep up with these kinds of major industry shifts, you can follow the latest market movements right here in our vTrader news hub.
How to Track and Interpret Hash Rate Data
Understanding the theory behind hash rate is one thing, but tracking it in real-time is where the magic happens. This is how you get ahead of the curve with actionable insights.
Fortunately, you don't need to be a data scientist to do this. A whole ecosystem of public tools, mainly blockchain explorers and specialized data aggregators, lays all the necessary information right at your fingertips.
These platforms give you a front-row seat to a network's hash rate over time, usually presented in easy-to-read charts. Think of it like a doctor reading an EKG—you’re looking at the vital signs of a blockchain, spotting trends, and diagnosing its overall health.
Reading the Hash Rate Charts
When you pull up a hash rate chart, you're looking at a direct measurement of two critical things: miner participation and network security. It's that simple.
A steady, upward trend is the gold standard. It’s a clear signal of a healthy, growing ecosystem where more miners are plugging in their hardware and investing their resources. That’s a network people believe in.
On the flip side, a sudden, sharp drop can be a major red flag. It might signal a mass exodus of miners due to unprofitability, a regulatory crackdown in a major mining country, or even a massive power outage affecting a mining hub. This kind of data provides crucial context for what’s happening in the market.
Don’t just look at the total hash rate; look at its distribution. If too much of that computing power gets concentrated in just a handful of mining pools, it opens the door to centralization risks. In theory, this could make the network more vulnerable.
The chart below from Coinwarz shows Bitcoin's historical hash rate, and its growth is nothing short of incredible.
That powerful, consistent climb you see isn’t just a line on a graph. It represents a massive, ever-increasing investment in the network's security infrastructure.
The growth has been truly exponential. In September 2025, the Bitcoin network's computational power screamed past an all-time high of 1,441.84 exahashes per second (EH/s). To put that in perspective, it's a nearly one-million-fold increase since 2017. You can see more on this exponential growth on Coinwarz.com. This raw power is what makes the network so incredibly robust against attacks.
By getting comfortable with these tools, you move past just knowing what a hash rate is and start using it as a practical gauge for a blockchain's real-world strength and stability. Ready to put this into practice? You can explore crypto data for all sorts of assets right on our platform.
Your Hash Rate Questions, Answered
Let's clear up a few common questions that pop up when people start digging into hash rate. Think of this as a quick-fire round to lock in what we’ve covered.
Does a Higher Hash Rate Make My Transactions Faster?
Not really, no. A massive network hash rate is great for security and keeps the block production humming along at a steady pace—like Bitcoin’s target of every 10 minutes. But it won't make your specific transaction clear any faster.
What actually speeds up your transaction is the fee you attach to it. If the network is busy, a higher fee gives miners a reason to pick your transaction out of the crowd and stick it in the next block. That’s your fast pass.
What Happens If a Network’s Hash Rate Suddenly Drops?
A sudden, steep drop in hash rate can be a bit scary. It temporarily makes the network cheaper to attack with a 51% attack because an attacker needs less power to gain control.
But blockchains are built for this. After a certain number of blocks, the mining difficulty automatically adjusts itself downward. This makes it easier for the remaining miners to find blocks, keeping the system stable. Big drops like this are often a signal of something happening in the real world, like a country banning mining or a massive power grid failure in a mining hotspot.
It's worth remembering: hash rate is purely a Proof-of-Work (PoW) thing. Networks like Ethereum now run on Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where security comes from validators staking their own crypto, not from raw computing power.
If you’re ever tripped up by terms like PoW vs. PoS, a good Web3 Dictionary can be a lifesaver. It’s a great way to get straight answers without the jargon.
At vTrader, we believe that a deep understanding of core concepts like hash rate is the first step toward confident trading. Explore our commission-free platform and continue your learning journey today. Get started at https://www.vtrader.io.

Steve Gregory is a lawyer in the United States who specializes in licensing for cryptocurrency companies and products. Steve began his career as an attorney in 2015 but made the switch to working in cryptocurrency full time shortly after joining the original team at Gemini Trust Company, an early cryptocurrency exchange based in New York City. Steve then joined CEX.io and was able to launch their regulated US-based cryptocurrency. Steve then went on to become the CEO at currency.com when he ran for four years and was able to lead currency.com to being fully acquired in 2025.




