Think of a Bitcoin address as your personal, digital mailbox for receiving Bitcoin. It's a unique string of characters you can safely share with anyone who wants to send you BTC—kind of like giving someone your bank account number for a wire transfer.
Your Digital Mailbox for Bitcoin Explained

Let's use an analogy. Imagine the entire Bitcoin network is a giant, global postal service. Within this system, your Bitcoin wallet is your personal post office—it's where you manage all your digital mail. Your private key is the only key that can open that post office, giving you exclusive access to send out mail (or in this case, Bitcoin).
So, what’s the Bitcoin address? It’s simply your publicly known mailbox number. Anyone can see it and use it to send you crypto, but only you, with your private key, can get inside your "post office" to access what they've sent.
The Core Components of Your Crypto Mail System
This trio—address, wallet, and private key—is the bedrock of Bitcoin's security. It's a simple but powerful system.
Here’s how it all fits together:
- Public Address: This is the destination for incoming funds. It's a unique string of 26 to 35 alphanumeric characters that's completely safe to share.
- Crypto Wallet: This is your command center. It holds your private keys and interacts with the Bitcoin blockchain to manage your funds and create transactions.
- Private Key: This is the ultimate proof of ownership. It's a secret code that authorizes you to spend the Bitcoin associated with your address. Never, ever share this with anyone.
One common misconception is that a Bitcoin address "holds" your coins. In reality, it's just a public record on the blockchain that shows a specific balance. The private key is what unlocks the ability to move that balance.
The Bitcoin network is a bustling ecosystem, processing over 270,000 transactions daily across a vast number of active addresses. This constant flow highlights just how many of these digital mailboxes are being used every single day.
Getting this concept down is your first big step toward using Bitcoin with confidence. To build on this foundation and explore other core crypto concepts, check out the resources at the https://www.vtrader.io/en-us/academy. For a deeper dive into how Bitcoin addresses work, this guide offers a fantastic breakdown: What Is a Bitcoin Address? Your Complete Guide.
How Is a Bitcoin Address Actually Made?
Ever wondered where your Bitcoin address comes from? It doesn't just appear out of thin air. It’s the end result of a clever, one-way cryptographic process that happens behind the scenes in your wallet, all designed to keep your funds safe.
The whole thing starts with your private key. This is the holy grail—a massive, randomly generated number that’s for your eyes only. Think of it as the ultimate master key; it’s the one thing that gives you the power to actually spend your Bitcoin.
From this super-secret private key, your wallet uses some heavy-duty math to generate a matching public key. The two are linked forever. It’s a bit like a physical key and a specially designed lock. Your private key is the only thing that can open the lock (your public key), which is visible to everyone but totally secure without its match.
From Public Key to Public Address
But we're not quite done yet. While the public key is born from the private key, it's not actually the thing you give out to people. To add another layer of security and make it a bit more practical, the public key goes through one final step: a hashing function.
This function essentially crunches the public key down into a shorter, neater string of characters. What comes out the other side is your shareable Bitcoin address.
The real magic here is that this whole process is a one-way street. You can easily go from private key to public key, and from public key to address. But going backward? It's mathematically impossible to reverse-engineer a private key from a public address.
This cryptographic shield is what the entire Bitcoin network is built on. It’s how your address can be totally public knowledge while your funds remain locked down and secure, because nobody can ever work their way back to the secret key that controls them.
Your Wallet Handles the Hard Part
The best part? You don't need to be a math genius or a cryptographer to make any of this happen. Your crypto wallet, whether it’s on vTrader or somewhere else, does all the heavy lifting for you in an instant.
Here’s a quick look at what’s happening under the hood:
- Private Key Generation: When you set up a new wallet, it generates a brand new private key.
- Public Key Derivation: It immediately derives the corresponding public key from that private one.
- Address Creation: Finally, it hashes that public key to spit out your unique, shareable Bitcoin address.
Every single time you hit "receive" to get a new address, your wallet runs through these steps in a flash. It’s an elegant system that gives you military-grade security without you having to lift a finger, so you can send and receive Bitcoin with complete peace of mind.
Understanding Different Bitcoin Address Formats
You might have noticed that not all Bitcoin addresses look the same. This isn't just a cosmetic difference—the format you use can actually change how much you pay in transaction fees and which wallets you can use.
Think of it like this: a .docx file and a .pdf both hold text, but they’re built differently and have their own pros and cons. Bitcoin has gone through a similar evolution, leading to a few different address formats over the years.
Getting a handle on these formats is the key to making sure your transactions are cheap and don't hit any snags. While there are a handful of them out there, you'll really only run into three main types. Each one represents a different stage in Bitcoin's development, offering its own mix of efficiency and compatibility.
This visual breaks down how the core pieces—the private key, public key, and the address itself—are structured. It's a great illustration of the cryptography that keeps everything secure.
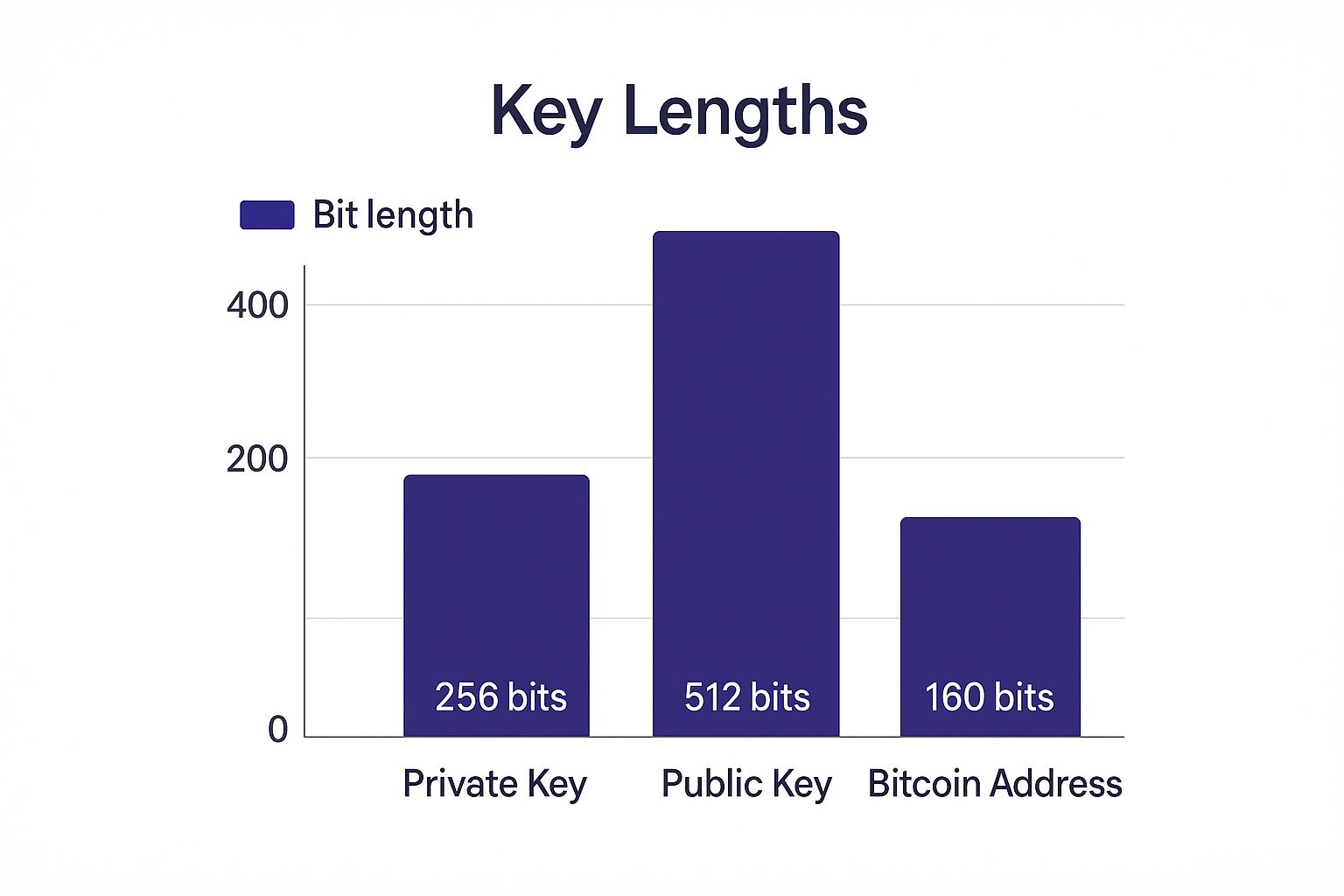
As you can see, the private and public keys are the heavy lifters in the background. The final address you see and use is a much shorter, compressed version designed for everyday use.
The Main Bitcoin Address Types
Let's cut to the chase and look at the three formats you absolutely need to know. The easiest way to tell them apart is by the very first character.
- Legacy (P2PKH): These are the OGs of Bitcoin addresses. They always start with the number '1'. While they work with just about every wallet, even the really old ones, they come with the highest transaction fees. They're reliable, but not the most efficient choice anymore.
- SegWit Compatible (P2SH): Think of these as the bridge to modern Bitcoin. Addresses starting with a '3' are clever because they're backward-compatible with older systems but still manage to offer some fee savings. It's a solid middle-ground option.
- Native SegWit (Bech32): This is the current gold standard. These addresses begin with 'bc1' and give you the lowest possible transaction fees and quicker processing times. Pretty much all modern platforms, including vTrader, use them, though some very old services might not have caught up yet.
To make it even clearer, let's compare them side-by-side.
Comparing Bitcoin Address Formats
This table breaks down the key differences between the formats at a glance, so you know exactly what you're working with.
| Address Format | Starts With | Key Benefit | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy (P2PKH) | 1 |
Maximum compatibility | Sending to very old wallets that don't support new formats. |
| SegWit (P2SH) | 3 |
Backward compatible, lower fees | A good middle-ground for compatibility and savings. |
| Native SegWit (Bech32) | bc1 |
Lowest fees, fastest speed | Everyday use on modern wallets and exchanges. |
For most people, the choice is simple: go with Native SegWit whenever you can.
Why Address Formats Matter for You
This isn't just a technicality—it directly impacts your crypto experience. Using a modern format like Native SegWit means your transactions cost less and get confirmed faster. In fact, you can save up to 30-40% on fees compared to a Legacy address. That's a huge saving that really adds up.
This concept of network fees isn't unique to Bitcoin, either. You see the same principles at play with other major cryptocurrencies, like when you’re trying to understand Ethereum gas fees.
The bottom line? Knowing which address to use helps you avoid overpaying and ensures your funds arrive without a hitch. The good news is that most modern wallets like vTrader handle this for you by default, always generating the most efficient address type available.
Best Practices for Keeping Your Address Secure

Getting a handle on what a Bitcoin address is and how it works is only half the battle. The other, far more important half is knowing how to lock down the funds sitting in it. When it comes to crypto, you are your own bank—which means security starts and ends with you.
The absolute number one rule is to protect your private key at all costs. Think of it as the master key to your entire crypto vault. If that key is lost, stolen, or compromised, your Bitcoin is gone forever. There's no customer service line to call. This is the bedrock principle of self-custody.
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
One of the biggest security decisions you'll make is choosing between a "hot" and a "cold" wallet. A hot wallet stays connected to the internet, like a mobile app or browser extension, making it super convenient for frequent trading. A cold wallet, on the other hand, is kept completely offline, giving you the strongest possible defense against online threats like hacking and malware.
While convenient, that constant internet connection makes hot wallets inherently riskier. As of 2025, internet-connected hot wallets account for a staggering 78% of all crypto wallets, with offline cold wallets making up the other 22%. But the tide is turning. With security concerns on the rise, hardware wallet sales have jumped by 31%, showing a clear shift toward tougher protection. You can find more insights on wallet trends over at coinlaw.io.
If you’re holding any significant amount of Bitcoin, a hardware wallet—a type of cold wallet—is the gold standard. It keeps your private keys on a secure, physical device, ensuring they never even touch an internet-connected computer.
Your private key should never be stored digitally where it can be compromised. Don't save it in cloud storage, email drafts, or on your computer's desktop. Write it down on paper and store it in multiple secure, physical locations.
Never Reuse a Bitcoin Address
Here's a pro-tip that will seriously boost both your security and your privacy: generate a new Bitcoin address for every single transaction you receive. Sure, you can reuse addresses, but doing so leaves a trail of breadcrumbs on the blockchain. Anyone can follow that trail to link all of your transactions together.
This practice makes it way too easy for snoops to analyze your financial activity, guess how much you're holding, and maybe even figure out who you are. By using a fresh address for each payment, you break those links and make your transaction history much harder to trace. This approach is a core part of our own commitment to user security, which you can read about in the vTrader privacy policy.
The good news is that most modern wallets, including ours at vTrader, handle this for you automatically. It’s a simple step that goes a long way in protecting your financial privacy.
Getting and Using a Bitcoin Address on vTrader
Alright, enough with the theory. Let's get down to brass tacks and see how this all works in the real world. Getting your first Bitcoin address on vTrader is a piece of cake—we’ve designed it to be simple and secure so you can start sending and receiving crypto with confidence.
Behind the scenes, your vTrader wallet does all the heavy lifting. Every time you need to receive Bitcoin, the platform spins up a brand new, unique address for that single transaction. This isn't just a neat trick; it's a critical privacy feature that keeps prying eyes from easily connecting the dots of your financial activity on the blockchain.
How to Receive Bitcoin on vTrader
Your first move in the crypto space will likely be receiving some funds. This all begins with generating an address you can share with the sender, and it only takes a few seconds.
- Head to Your Wallet: Log into your vTrader account and click on the 'Wallet' section.
- Pick Bitcoin (BTC): You’ll see a list of your cryptocurrencies. Just select Bitcoin.
- Click 'Receive': Boom. The system instantly creates a fresh, secure Bitcoin address just for you.
You'll see your new address pop up on the screen, both as a long string of characters and as a handy QR code for quick mobile scans.
Here’s a look at the receive screen on vTrader, showing both the QR code and the full address you can copy.
See that big "Copy" button? Use it. It's the best way to share your address without making any costly typos.
Sending Bitcoin Securely
When it's time to send Bitcoin, you need to be extra careful. The most important part is getting the recipient's address absolutely right.
Instead of trying to type it out by hand, always, always use copy-and-paste. This one simple habit dramatically cuts down the risk of human error. If even a single character is wrong, your Bitcoin could be sent to a dead-end address or, worse, someone else's wallet. And since blockchain transactions are final, those funds would be gone for good.
Security Tip: After you paste the address, take two seconds to double-check the first four and last four characters. This quick scan is your best defense against a nasty scam called "address poisoning," where a fraudster sends you a tiny transaction from a lookalike address, hoping you'll accidentally copy it from your history later on.
Once you’ve pasted and verified the address, just punch in the amount of BTC you want to send. vTrader will give you one final confirmation screen showing all the details—the address, the amount, and any network fees. This is your last chance to catch a mistake before you hit send.
After you've sent some BTC and maybe received a bit more, you might be interested in learning how to sell Bitcoin on vTrader to realize your gains.
Debunking Common Myths About Bitcoin Addresses

To really get a handle on what a Bitcoin address is, we first have to bust a few myths. A lot of people new to the space stumble over these, which can lead to some expensive mistakes or just a wonky understanding of how Bitcoin actually works. Let's clear the air.
One of the most common misconceptions is that Bitcoin is totally anonymous. The truth is, it's pseudonymous. While your name and address aren't attached to your Bitcoin address, every single transaction gets etched into the public blockchain forever. If anyone ever connects your identity to one of your addresses, your entire financial history on the chain is an open book.
Your Address Doesn't Actually Hold Your Coins
Here's another one that trips people up: thinking that your Bitcoin is literally inside your address, like cash in a digital safe. That's not quite how it works. Your coins are just records on the blockchain, and your address is really just a public label that points to them.
Think of a Bitcoin address like a public PO Box number. Anyone can see the box and what's being sent to it, but only the private key can actually open it to access and spend what's inside. Without that key, the address is just a string of random characters.
Understanding this difference is everything. It hammers home the point that protecting your private key—not just the public address—is the only thing that keeps your Bitcoin safe.
People also get "address" and "wallet" mixed up. They're connected, but they aren't the same thing. A wallet is the app or device that holds your private keys and lets you create and manage all your different addresses.
Finally, let’s knock down two more quick but crucial myths:
- Myth: An address can expire. Truth: Bitcoin addresses last forever. They never expire and can receive funds at any time.
- Myth: It's fine to reuse the same address. Truth: You can, but it’s a bad idea for your privacy. The smart move, and the growing standard, is to generate a fresh bitcoin address for every single transaction. This makes it much harder for anyone to connect the dots on your spending. You can dig deeper into this and other privacy trends by checking out the latest Bitcoin statistics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Getting the hang of Bitcoin addresses can spark a few last-minute questions. Here are some quick answers to the most common ones, so you can handle your BTC like a pro.
Can I Have More Than One Bitcoin Address?
Yes, and you absolutely should. In fact, think of it as a golden rule for protecting your privacy.
Using a fresh, unique address for every single transaction you receive makes it incredibly difficult for prying eyes to connect the dots on your financial activity. Most modern wallets, including vTrader, automatically generate a new address for you every time you need one.
What Happens If I Send BTC to the Wrong Address?
This is where you need to be extremely careful. Bitcoin transactions are final—once they're sent, they're gone for good.
If you accidentally send your funds to an incorrect address, there’s no "undo" button or customer service line to call. The funds are likely lost forever. This is precisely why you should always copy and paste addresses and give them a quick double-check before confirming the transaction.
Key Takeaway: Always verify the first and last four characters of any Bitcoin address before you hit send. This simple habit is your best defense against a costly, irreversible mistake.
Does Uppercase and Lowercase Matter?
That all depends on the type of address you're using.
Older formats, like Legacy (1...) and SegWit Compatible (3...) addresses, are case-sensitive. You have to copy them exactly as they appear, or the transaction will fail. Newer Native SegWit (bc1...) addresses, however, aren't case-sensitive, which is a nice little feature that helps cut down on user error.
If you've got more questions on crypto, we've got answers. Feel free to dive into our extensive vTrader FAQ page.
Ready to manage your crypto with zero trading fees? Join vTrader today to generate your secure Bitcoin address and start trading smarter. Sign up at https://www.vtrader.io and begin your journey.

Steve Gregory is a lawyer in the United States who specializes in licensing for cryptocurrency companies and products. Steve began his career as an attorney in 2015 but made the switch to working in cryptocurrency full time shortly after joining the original team at Gemini Trust Company, an early cryptocurrency exchange based in New York City. Steve then joined CEX.io and was able to launch their regulated US-based cryptocurrency. Steve then went on to become the CEO at currency.com when he ran for four years and was able to lead currency.com to being fully acquired in 2025.




