Forget everything you’ve heard about blockchain being complicated. At its heart, the concept is surprisingly simple.
Imagine a shared digital notebook. This notebook isn't stored in one place; instead, it's copied and spread across thousands of computers. Every time someone adds a new entry, it’s recorded on every single copy. And here’s the kicker: once an entry is made, it can never be altered or erased. This creates a permanent, rock-solid record of information that everyone can trust.
Your First Look at Blockchain Technology
Think of blockchain as a whole new way to keep records. Traditionally, a single entity—like a bank—controls its own private ledger of transactions. Blockchain flips that model on its head. The ledger is shared among everyone in the network, cutting out the need for a central authority. This empowers people to interact directly and securely, without a middleman.
This powerful idea was first introduced back in 2008 by the still-anonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, right alongside the creation of Bitcoin. It didn't take long for the world to catch on. The global blockchain market was valued at around $31.28 billion, and some projections see it soaring to an incredible $1,431.54 billion by 2030. That’s not just growth; it’s an explosion.
Understanding the Three Pillars of Blockchain
To really get a feel for what blockchain is all about, you need to know the three core principles that make it all work. These pillars are what give the technology its strength, making it not only efficient but also incredibly reliable and almost impossible to cheat.
- Decentralization: No single person or company is in charge. Because the ledger is copied and shared across a massive network, there's no single point of failure. One person can't change the rules or shut things down.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is locked into the blockchain, it’s sealed with powerful cryptography. It can't be changed or deleted. Ever. This creates a perfect, unchangeable audit trail that anyone can verify.
- Transparency: While your personal identity can remain private, the transactions themselves are typically open for everyone on the network to see. This shared visibility builds massive trust because everyone is looking at the same source of truth.
To make this even clearer, let's break down these foundational concepts.
Core Blockchain Concepts at a Glance
| Concept | Simple Explanation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | No single boss. The network is run by its users. | Makes the system more secure and resistant to censorship or control. |
| Immutability | Once written, records can't be changed. | Creates a trustworthy and permanent history of all transactions. |
| Transparency | Everyone can see the transactions on the public ledger. | Builds trust among users, as all activity is verifiable. |
These three pillars work together to create something pretty special.
In simple terms, blockchain provides a way for untrusting parties to agree on the state of a shared database without needing a middleman. It’s a machine for creating trust.
While these ideas might seem a bit abstract at first, they are the very foundation of a more secure digital economy. If you're curious to see how these principles come to life in the world of crypto, our guides in the vTrader Academy are a great next step.
How a Single Transaction Joins the Blockchain
So, what really happens when you send crypto to a friend? It's easy to picture it as a simple digital transfer, but behind the scenes, a fascinating and incredibly secure process kicks off the moment you hit "send." Your transaction is about to become a permanent, unchangeable part of the blockchain.
It all starts when your transaction—containing the sender, receiver, and amount—is broadcast to a massive, global network of computers. These computers, known as nodes, form the backbone of the blockchain, and their job is to keep the shared ledger honest.
The Verification and Bundling Process
Once out on the network, your transaction lands in a sort of digital waiting room called the mempool, along with tons of other recent transactions. From there, special network participants called miners (or validators in newer systems) pick it up to make sure everything is legitimate. They run a series of checks to confirm you actually have the funds and the authority to send them.
After getting the green light, your transaction gets bundled with hundreds, maybe even thousands, of others into a new, unconfirmed "block." A good way to think about it is like putting a stack of notarized documents into a sealed briefcase, ready to be added to the official public archives.
This whole flow, from your initial request to its final addition, makes sure every single action on the network is checked and approved by many different parties. The image below breaks down this three-step journey.
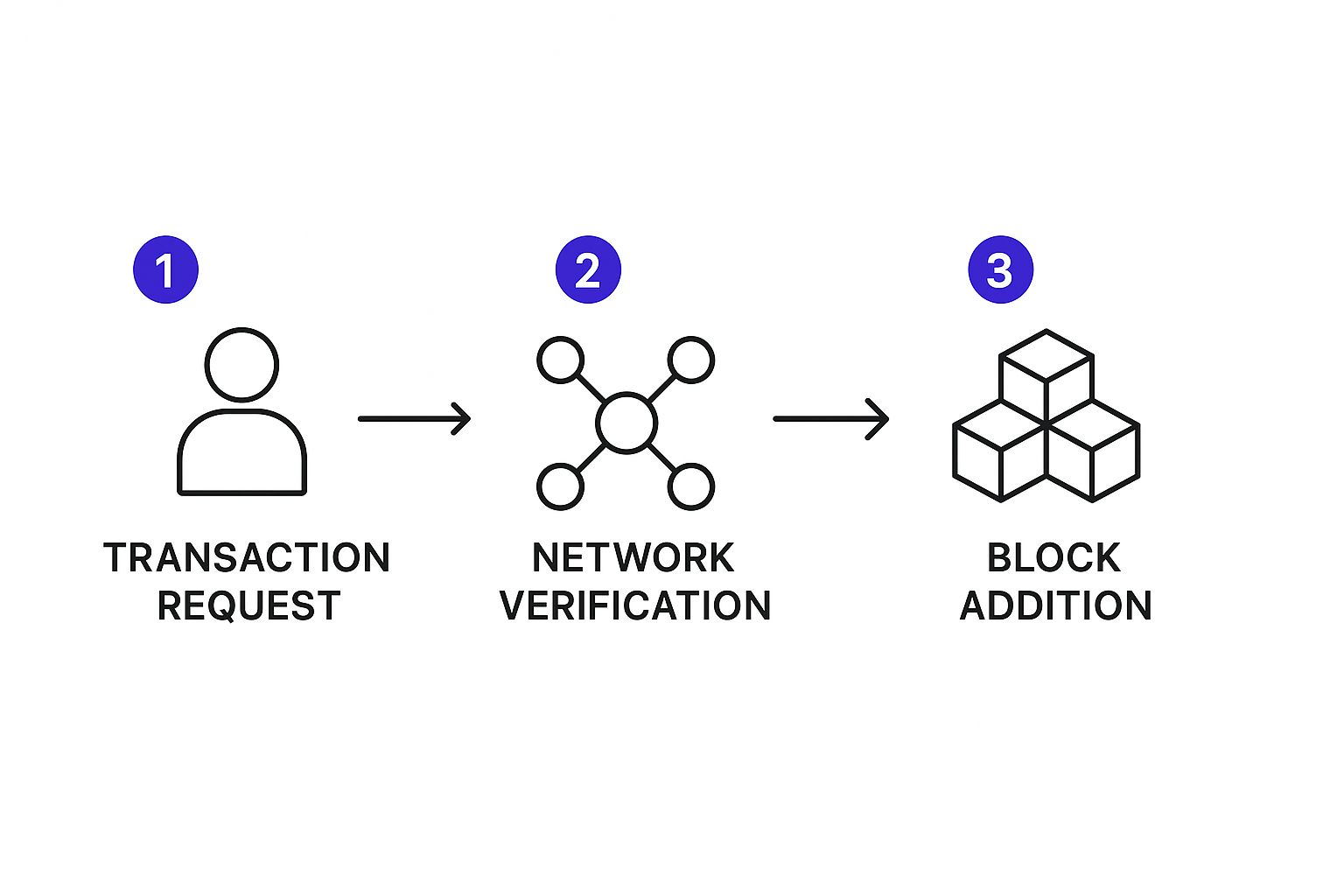
As you can see, a user’s request has to pass muster with the distributed network before it ever gets added to the chain. It’s this decentralized security model that sits at the very heart of blockchain.
Forging the Unbreakable Chain
Now for the really clever part. To add this new block to the existing blockchain, miners have to solve an incredibly difficult mathematical puzzle. This is the famous mining process you hear about with Bitcoin, and it requires a staggering amount of computing power. It’s also what makes the network so secure. The first miner to crack the puzzle gets the right to add the block.
Once a miner finds the solution, they announce it to the entire network. The other nodes quickly check their work, and if everyone agrees the solution is correct, the new block is officially attached to the end of the chain.
This is where the magic happens. Every block contains a unique cryptographic signature—a "hash"—that links it directly to the block before it. This creates a chronological and unbreakable chain. Trying to alter a past transaction would mean re-solving the puzzle for that block and every single block that came after it, which is a practically impossible task.
This interconnected structure is precisely what gives the ledger its famous immutability. You can trust it.
With that, your transaction is now a permanent fixture on the blockchain. It's copied across thousands of nodes worldwide, meaning there’s no single point of failure and the record is protected from anyone trying to tamper with or delete it. This elegant system of verification, bundling, and cryptographic linking is the engine that drives blockchain, delivering security without ever needing a bank or central authority.
Exploring the Core Parts of a Blockchain

To really get what makes blockchain tick, you have to pop the hood and look at the engine. The core components work together like gears in a complex watch, creating a system that’s secure, transparent, and incredibly tough to break. Once you see how they connect, it all starts to make sense.
At its heart, a blockchain has four key elements, all working in perfect harmony. Each one has a critical job to do, ensuring the entire network stays honest and reliable.
These pieces are:
- Blocks: Think of them as the individual pages in a digital record book.
- Nodes: The network of computers that protect and maintain that book.
- The Ledger: The complete, shared, and distributed record book itself.
- Consensus Mechanism: The rulebook everyone agrees on to add new pages.
Let’s pull each one apart to see how they fit into the bigger picture.
Blocks The Digital Containers of Data
Every blockchain is literally a chain of blocks. These are just digital containers that hold information. Each block is packed with a batch of recent transactions, a timestamp showing when it was created, and a unique cryptographic code known as a hash.
Here’s the clever part: every block also contains the hash of the one that came before it. This is what chains them all together in a perfect, unbreakable sequence. If someone tried to alter a past transaction, the block's hash would change, instantly breaking the chain and alerting the entire network to the fraud. It’s a digital tripwire.
Nodes The Guardians of the Network
The real power of a blockchain comes from its nodes—the thousands of individual computers run by people all over the world. Picture them as a global team of independent accountants, where every single one holds an identical copy of the same financial ledger.
These nodes are the ones keeping the whole system honest. They validate transactions, confirm new blocks, and make sure everyone on the network is following the rules. The more nodes a network has, the more secure and decentralized it becomes.
This structure means there’s no central server to hack or shut down. If one node goes offline, the network doesn’t even blink; it’s held up by all the other participants. This is the "distributed consensus" that makes public blockchains so resilient.
For anyone trading digital assets, understanding this built-in integrity is crucial. It’s why platforms prioritize transparency and clear operational standards, much like the trust built by a straightforward refund policy.
Finally, the consensus mechanism is the rulebook that all these nodes agree to follow. It’s how they collectively decide to approve transactions and add new blocks to the chain. The most famous one is Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work (PoW), where nodes (called "miners") solve complex math puzzles. Other methods exist, like Proof-of-Stake (PoS), but they all share the same goal: to get everyone to agree on a single source of truth without needing a boss to tell them what to do.
Why Blockchain Is a Game-Changing Technology

It’s one thing to get how blockchain works, but the real "aha" moment comes when you see why it’s such a big deal. The technology’s true power isn’t in the theory—it’s in the real-world problems it solves. This isn't just another database; it's a completely new way to build trust and operate efficiently.
The magic comes from its core design. Instead of tucking data away in one central place, blockchain scatters it across a huge network. This simple shift creates a system that’s naturally more secure, transparent, and incredibly difficult to cheat.
A New Standard for Security and Trust
Think about how most data is stored today—usually on a single server, which is like putting a giant bullseye on it for hackers. Blockchain gets rid of that single point of failure. With the ledger copied across thousands of computers, there’s no central honeypot to attack.
This built-in security gets even stronger with immutability. Once a transaction is locked into a block, it’s sealed with cryptography and becomes a permanent part of the chain. Trying to alter it would set off alarm bells across the entire network. This creates a rock-solid, unchangeable audit trail for everything from financial trades to tracking a product's journey.
Because every participant has their own copy of the exact same ledger, blockchain establishes a single, shared source of truth. This level of transparency gets everyone on the same page, cutting down on disputes and building real confidence between parties.
We're already seeing this shift from a niche idea to core business infrastructure. Over 47% of global enterprises are already using blockchain in their day-to-day operations. In finance, that number jumps to 87% of firms using it to make their processes smoother. Networks like Ethereum now handle millions of transactions every single day, showing just how fast this technology is catching on.
Driving Efficiency and Lowering Costs
One of blockchain’s most practical superpowers is its ability to kick middlemen to the curb. Take sending money overseas, for example. A normal wire transfer has to hop between multiple banks and clearinghouses, taking days and racking up fees at every stop.
With blockchain, that same transaction can be done directly between two people in minutes, often for pennies. By cutting out all the go-betweens, it drastically speeds things up and slashes costs. This isn't just for money transfers—it’s happening in real estate, music royalties, and countless other industries.
The advantages are pretty clear:
- Superior Security: A decentralized network is infinitely harder to attack than a single server.
- Radical Transparency: Everyone with permission sees the same information, keeping things honest.
- Greater Efficiency: Cutting out intermediaries means faster settlement times and lower fees.
- Improved Traceability: You can follow an asset’s journey from its origin with total certainty.
As blockchain continues to evolve, staying on top of the latest trends is a must for any serious trader. Keeping up with market insights on the vTrader news hub can help you spot how these tech shifts are opening up new doors.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrency
While cryptocurrency was blockchain’s big debut, its real power goes way beyond digital cash. It’s better to think of blockchain not as just a financial tool, but as a new way of building trust and transparency into pretty much any industry you can imagine. Companies are finally tackling decades-old problems that once seemed impossible to fix.
One of the biggest game-changers is in supply chain management. Picture trying to track a head of lettuce from a farm in one country all the way to a grocery store shelf in another. That journey involves dozens of shippers, handlers, and inspectors, each with their own separate paperwork. It’s a messy, fragmented trail that’s just asking for errors and fraud.
With blockchain, you get a single, shared source of truth. Every time that lettuce changes hands, the event is logged as a permanent, time-stamped block on the chain. Now, everyone from the farmer to the final consumer can see its entire journey, verifying its origin, authenticity, and handling conditions in real-time.
Transforming Industries with Trust
This same core idea—replacing slow, clunky systems with a secure, shared ledger—is shaking up other sectors.
- Healthcare: Patient data is incredibly sensitive and is usually locked away in different hospitals and clinics. Blockchain can create secure, patient-controlled health records, giving you the power to grant doctors temporary access to your complete medical history.
- Voting Systems: By recording each vote as an anonymous but verifiable transaction, blockchain can create election systems that are transparent and nearly impossible to tamper with.
- Intellectual Property: Digital artists can "mint" their work as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) on a blockchain. This creates a permanent, public record of ownership that ensures they get credit and royalties for their work.
At its heart, blockchain offers something simple: an unchangeable record of events that everyone involved can trust without needing a middleman to vouch for it. This foundation of trust is what streamlines complex agreements and secures digital assets.
We're seeing these uses take off globally. Asia has become a major hub, with around 263 million crypto users and accounting for 32% of worldwide digital asset development. Meanwhile, North America still commands the largest trading volume. This widespread interest just goes to show how central this technology is becoming to the modern economy. You can find more on these blockchain adoption statistics and facts.
Beyond just proving ownership, these digital assets open up new financial strategies. For traders on platforms like vTrader, understanding how assets like NFTs fit into the bigger picture, including getting a solid grasp of how staking crypto works, is more important than ever. As the technology matures, these applications are moving from the fringe to the forefront of a more secure and efficient digital world.
Common Questions About Blockchain Technology
As you start digging into blockchain, it's natural for questions to pop up. It’s a powerful technology, but it's often wrapped in confusing technical jargon and a fair bit of myth. Let's cut through the noise and tackle some of the most common questions head-on.
Think of this as your go-to guide for solidifying your understanding. We’ll cover everything from how blockchain relates to Bitcoin to its real-world limits and where it's headed next.
Is Blockchain the Same as Bitcoin?
This is easily the most common question, and the answer is a firm no. They are definitely related, but they are not the same thing at all.
Here’s a simple way to think about it: imagine blockchain is the operating system, like the iOS or Android on your phone. Bitcoin, in this case, was just the very first killer app built to run on that system.
Blockchain is the underlying ledger technology that makes secure, decentralized record-keeping possible. Bitcoin is simply one specific cryptocurrency that uses a blockchain to keep track of who owns what. While Bitcoin pioneered the technology, thousands of other digital assets and systems have since been built on various blockchains.
Is Blockchain Technology Completely Secure?
The core design of a blockchain is incredibly secure. Because it's decentralized and locked down with heavy-duty cryptography, it's almost impossible for a single person to go back and alter the historical record. To change a past transaction, you'd need an insane amount of computing power—so much that it's not feasible on major networks.
But is it "completely secure"? That's a bit of an overstatement. Vulnerabilities can, and do, exist in the ecosystem built around the blockchain itself.
The chain itself is robust, but the applications connected to it are not always foolproof. Weaknesses can be found in crypto exchanges, digital wallets, and the code of smart contracts, which can be exploited by attackers.
This means that while the fundamental tech is solid, the safety of your assets often comes down to the platforms and tools you choose to interact with it.
What Are the Main Disadvantages?
For all its strengths, blockchain isn't the perfect fix for every problem. It comes with a few significant hurdles that developers are working hard to overcome.
- Scalability: Major blockchains can get jammed up. During busy periods, this traffic jam leads to slow transaction speeds and high fees, which can make small payments totally impractical.
- Energy Consumption: Some of the biggest blockchains, like Bitcoin, use a model called "Proof-of-Work" that requires a massive amount of electricity to stay secure. This environmental footprint is a major point of criticism.
- Complexity and Adoption: Let's be honest—using blockchain apps can still feel clunky and intimidating for the average person. A lack of user-friendly design and clear regulations often makes people and businesses hesitant to jump in.
What Is the Future of Blockchain Technology?
The future of blockchain is looking way bigger than just finance and crypto. Its real power lies in creating a trusted, shared source of truth, and that's finding a home in all sorts of industries. We're seeing huge growth in areas like supply chain management to prove products are authentic, healthcare to keep patient data secure, and even systems for tamper-proof digital identities.
At the same time, major innovations are tackling its early growing pains. New consensus models and "Layer 2" solutions are making blockchains faster, cheaper, and much more energy-efficient. As the tech gets easier to use and more accessible, many experts believe it will become a fundamental part of the internet's plumbing, powering a new wave of decentralized apps (dApps) and safer online experiences.
As you keep learning, having more specific questions is a great sign. For more detailed answers, you can always check out the comprehensive FAQ section on vTrader for extra insights.
Ready to put your knowledge into action? With vTrader, you can trade Bitcoin, Ethereum, and over 30 other cryptocurrencies with zero commission fees. Sign up today and get a $10 bonus to start building your portfolio. Join us at https://www.vtrader.io.

Steve Gregory is a lawyer in the United States who specializes in licensing for cryptocurrency companies and products. Steve began his career as an attorney in 2015 but made the switch to working in cryptocurrency full time shortly after joining the original team at Gemini Trust Company, an early cryptocurrency exchange based in New York City. Steve then joined CEX.io and was able to launch their regulated US-based cryptocurrency. Steve then went on to become the CEO at currency.com when he ran for four years and was able to lead currency.com to being fully acquired in 2025.


